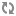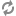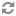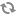Present Perfect
Present Perfect Tense Kullanımı ve Cümle Yapısı
Present Perfect Tense geçmişte belirsiz bir zamanda yapılmış bir eylemi ifade etmek için kullanılır. Eylemin ne zaman yapıldığı veya olduğu önemli değildir. Her fiilin Present Perfect Tense hali iki öğeden oluşur: to have yardımcı fiilinin uygun şekli ve fiilin V3 (past participle) halidir. Üçüncü tekil şahıslar (he, she, it) ve tekil isimler için "has" yardımcı fiili kullanılır. Diğer şahıslar (I, you, we, they) ve çoğul isimler için "have" yardımcı fiili kullanılır. Yardımcı fiil olumlu, olumsuz ve soru cümlelerinde mutlaka bulunur. Bu yardımcı fiillerden sonra, fiilin V3 (past participle) hali kullanılır. Düzenli fiillerin V3 (past participle) hali fiil kökü+ed şeklinde yapılır, örneğin played, arrived, looked. Düzensiz fiiller için bu linkten Düzensiz Fiiller Tablosuna bakılabilir.
| Olumlu | ||
| Subject | to have | past participle |
| She | has | visited. |
| Olumsuz | ||
| Subject | to have + not | past participle |
| She | has not (hasn't) | visited. |
| Soru | ||
| to have | subject | past participle |
| Has | she | visited? |
| Olumsuz soru | ||
| to have + not | subject | past participle |
| Hasn't | she | visited? |
To Walk, present perfect
| Olumlu | Olumsuz | Soru |
|---|---|---|
| I have walked | I haven't walked | Have I walked? |
| You have walked | You haven't walked. | Have you walked? |
| He, she, it has walked | He, she, hasn't walked | Has he, she, it walked? |
| We have walked | We haven't walked | Have we walked? |
| You have walked | You haven't walked | Have you walked? |
| They have walked | They haven't walked | Have they walked? |
Functions of the Present perfect
The Present Perfect is used to indicate a link between the present and the past. The time of the action is before now but not specified, and we are often more interested in the result than in the action itself.
The Present Perfect is used to describe
-
An action or situation that started in the past and continues in the present.
I have lived in Bristol since 1984 (= and I still do.) -
An action performed during a period that has not yet finished.
She has been to the cinema twice this week (= and the week isn't over yet.) -
A repeated action in an unspecified period between the past and now.
We have visited Portugal several times. -
An action that was completed in the very recent past, expressed by 'just'.
I have just finished my work. -
An action when the time is not important.
He has read 'War and Peace'. (= the result of his reading is important)
Note: When we want to give or ask details about when, where, who, we use the simple past.
Actions started in the past and continuing in the present
- They haven't lived here for years.
- She has worked in the bank for five years.
- We have had the same car for ten years.
- Have you played the piano since you were a child?
When the time period referred to has not finished
- I have worked hard this week.
- It has rained a lot this year.
- We haven't seen her today.
Actions repeated in an unspecified period between the past and now.
- They have seen that film six times
- It has happened several times already.
- She has visited them frequently.
- We have eaten at that restaurant many times.
Actions completed in the very recent past (+just)
- Have you just finished work?
- I have just eaten.
- We have just seen her.
- Has he just left?
When the precise time of the action is not important or not known
- Someone has eaten my soup!
- Have you seen 'Gone with the Wind'?
- She's studied Japanese, Russian, and English.